It is just two weeks ago that Apple recently unveiled their new 4G iPhone 5 mobile phone. As expected by most of the users, there were not many major things changed on the look and feel of the device. Whether you should buy the new iPhone 5 or not depends on which Version you are using at the moment. As much older it is as more will the user benefit from the technological evolution in smartphone hardware meanwhile. The new operating system iOS 6 will be also available to older iPhone versions.

One change is definitely the taller 4 inch display combined with an inner cpu hardware upgrade of the A6 processor chip evolution. But maybe the greatest new feature is its ability to use LTE 4G wireless standard. This feature is able to bring incredible fast internet connection speed into the smartphone and extends the limits of what is possible today with a mobile phone device connection interface.
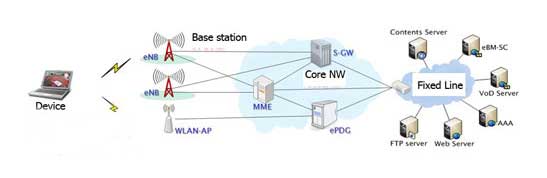
What is LTE?
LTE (Long Term Evolution) is a wireless standard, known as 3GPP. This standard is intended to further ensure the long-term competitiveness of UMTS and HSDPA networks. The development of LTE is to provide the suppliers of UMTS with HSDPA and HSUPA standards a cost evolutionary transition in the LTE standard.
The bandwidths of LTE
Unlike UMTS, the 3GPP standard supports different bandwidths. This allows providers to integrate the LTE standard also into their future networks. Its ability to integrate into various frequencies of 1.4, 3, 5, 10, 15 and 20 Mhz makes it very flexible. At a bandwidth of 20 MHz of peak data, rates up to 300 Mbit/s in downstream and to 75 Mbit/s in upload can be reached.
Especially the low latency allows users to run intense applications like VoIP, video telephony or playing online games. With UMTS, LTE customers will have further significant performance improvements compared with the current offer data rates for mobile Internet.
Why is LTE technology so much faster?
LTE is so much faster than the UMTS standards HSDPA and HSUPA because of the technology used with LTE. First of all, the LTE technology uses new encoding methods while downloading the OFDMA (Orthogonal Frequency Division Multiple Access) and uploading the SC-FDMA (Single-carrier frequency-division multiple access) scheme. Both schemes are very similar and will be used to reduce the power consumption of the LTE technology supporting devices. The use of OFDMA technology is furthermore the reason why the LTE technology is also called HSOPA (High Speed ODFM Packet Access).
The two techniques OFDMA and SC-FDMA are used to divide the available bandwidth into many small parallel carrier threads, the so called subcarriers. Since OFDMA was developed for multi-user operations, LTE providers can scale and assign specific bandwith to the user and adjust it dynamically to the users needs.
By splitting the total bandwidth used in the LTE technology, the standard is also less error prone to interferences and connection exception issues. Furthermore, this splitting ensures that access to higher bandwidth is available that can be consumed by users, who need more bandwidth on demand. A minor disadvantage of the LTE technology is that the encoding and decoding of subcarriers has an increased energy consumption.
