Sending or receiving mails is something that happens in such a seamless way that folks often think that it’s an automatic process, and seldom spare any time on figuring out how quickly the e-communication takes place.
Types of Email Servers
There is a very interesting technology behind the operation of email server. It consists of user-defined rules that decide how the server should respond to the location of a special mail. It also has a database of user’s account that the server identifies. It is formed by communication modules that handle the transit of emails from one server to another. Basically, email communication is performed by IMAP, POP3, or SMTP servers. The most widely used e-mail management tools are Mozilla Thunderbird, and Microsoft Outlook, but there are many other options available in the market as well. All of them work in a similar manner i.e. downloading the incoming mail from the server, such as AOL, Gmail, or Yahoo to the system.
How Email Communication Takes Place
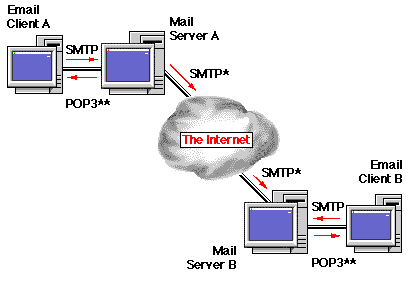
E-mail communication, which happens on the Internet via client server, is through a unique protocol. In simple words, the user in one system connects via protocol address via internet and the server on the other connected to the web takes care of serving or hosting web pages. In fact, these servers are programs, which run on high speed systems that are designed in such a way that they take care of the requests of billions of users. All the demands or actions are performed at the same time to those who access webpage or emails.
Role of SMTP Servers
When a mail is sent, the machine connects to your mail server that is a centralized computer, managing a specific email service. Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP) is the server that is responsible for sending messages. It transfers the emails from one server to another in several steps. Every mail transit will have 2 addresses- one for receiver’s and sender’s email addresses.
When the mail is sent out, the user connects to the SMTP server of the sender’s service and user’s address as well as recipient’s and message is transited by the user. This process becomes simpler if both the sender’s and receiver’s domain is same. Simplifying the explanation, an SMTP is just a pick-and-drop server that picks sender emails and drops them into the destined recipients.
Each domain refers to a unique Internet Protocol (IP) address and the server ensures that the mail addresses of the receiver belongs to that address and hands it over to IMAP or POP3 server that stores email IDs. Each email account has unique username and password and until the receiver logs in and checks the inbox, the message in the POP3 servers is reserved and saved in the email account.
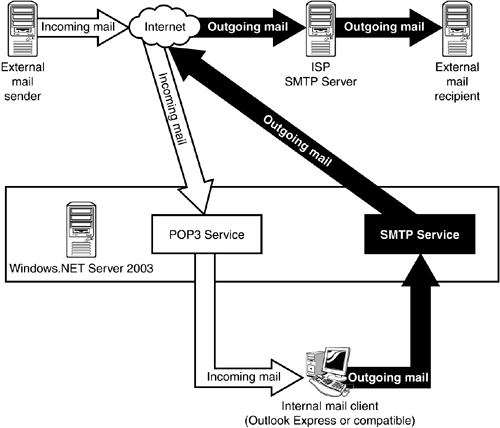
When is POP3 Used?
POP3 is largely linked with client programs like Thunderbird, Eudora, and Outlook. The email client screens out the server with provided login details. The POP3 scans the server looking for messages and downloads them to respective addresses. It removes your email soon from their server, once the messages get transferred to your account. In simpler words, POP3 will allow email for download and doesn’t keep a copy of the mail, once downloaded and delivered to client system. Hence, this is no
Filters
In an effort to stop spam, the mail servers have filters, which stop the client from sending duplicate mails to multiple email addresses. The spam filters running at servers can filter the mail into folders and sends warning to the email servers to delete the messages from it, which have already downloaded been.
Jolie a tech geek who has been working for About.com as the Web Hosting Guide, and reviewing various hosting companies and email hosting solutions. He has also done many comparisons of SMTP relays and written hundreds of technological guides.
Knowing the SMTP & POP3 Servers Better and Their Role in Email Communication Process,




Leah
Dec 16. 2012
Awesome article.
Phyd
Dec 24. 2012
Great overview for SMTP and POP3 email servers